ThanksDownload a SQlite editor https://sqlitebrowser.org/dl/ Shutdown Plex BACKUP first and then Open your Database: "C:\Users\YOUR-USERNAME\AppData\Local\Plex Media Server\Plug-in Support\Databases\com.plexapp.plugins.library.db" Update everything the used to be in drive C to the same exact path but on drive S UPDATE section_locations SET root_path = REPLACE(root_path, 'C:', 'S:') WHERE root_path LIKE 'C:%'; UPDATE media_parts SET file = REPLACE(file, 'C:', 'S:') WHERE file LIKE 'C:%'; Save the changes and exit your DB editor Restart Plex
Perfecting the art of rural communications using Linux, cloud, internet, wireless technologies since 1993
Move plex media
Fast secure erase of /dev/nvme0n1 using Ubuntu 22.04 LTS live
ThanksCheck your disk: sudo -i apt install nvme-cli nvme list Erase your disk: nvme format -s1 /dev/nvme0n1 Verify it is really all zeros: cmp /dev/nvme0n1 /dev/zero Verify with a progress bar: apt install pv pv /dev/nvme0n1 | cmp /dev/zero Really all zeros: cmp: EOF on after byte 512110190592, in line 1 Not really all zeros: /dev/zero differ: byte 449, line 1
No Get-FileHash? Use CertUtil instead. Built in Windows 7, 10, and 11 Without power tools.
You can also drop files on the tiny md5sumsMost are familiar with Get-FileHash .\Linux.iso What about an old or restricted windows system that does not have it and you cannot install programs? CertUtil is a another pre-installed Windows utility that can be used to generate hash checksums: certutil -hashfile .\Linux.iso SHA256 HashAlgorithm choices: MD2 MD4 MD5 SHA1 SHA256 SHA384 SHA512
Thanks
Thanks
YouTube Theatre view by default without extensions
Go to https://www.youtube.com
Open dev tools of the browser you are using (Press F12 or Right-click -> Inspect)
Select Console tab
Paste below code and Enter:
document.cookie = 'wide=1; expires='+new Date('3099').toUTCString()+'; path=/';
Thanks
grub2 can remember last choice
ThanksPut the following in /etc/default/grub GRUB_DEFAULT=saved GRUB_SAVEDEFAULT=true Then run: update-grub
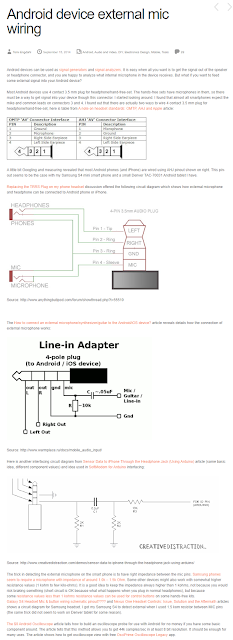
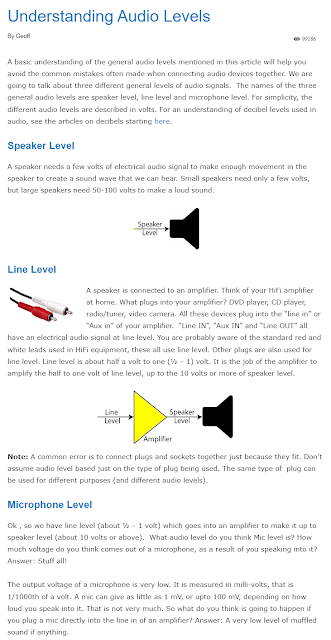
Connecting Line Level audio to Voice Meeter Potato over WiFi with VBAN Talkie and an old Android phone.
I needed to bring a high quality low noise unbalanced audio source into a Windows 11 PC from a mile away. I like very low cost or free when possible. Unbalanced audio over great distances has several challenges including the induction of noise, cable installation costs, installation time, signal loss, and other factors. Combining the following techniques worked well for me. Note that latency added by traversing multiple cellular and internet connections over VPN was not a concern for me for this project. Keeping the audio connection on a Local Area Network would reduce latency a lot but not match that of a simple cable, or FM radio.
Items Used:
- Voice Meeter Potato running on the PC (VBAN over VPN)
- Talkie running on the old android phone (LG V10)
- Optional VPN software. (WireGuard)
- Line to Mic adaptor Circuit (50K Pot and 10uF Capacitor Soldered in middle of a TRRS cable. (Made my own design to use parts I had laying around with Proto Circuit Simulator)
Helpful Videos:
2 Capacitors in Parallel for better audio quality
No analog level adjustment in this design, and I wanted it really hot, two components that I could cut an old cable in half and solder them in the middle.
Helpful articles:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Line_level
https://www.epanorama.net/blog/2014/09/15/android-device-external-mic-wiring/
Accurate time on Windows 11 and Windows 10
NTP for windows
Thanks ThanksAs a linux user, it bothered me that my windows 11 and windows 10 time was often several seconds off. For dual booting you might want to change the hardware clock to UTC. Sugest only this combined with NTP for windows Run cmd as admin, install NTP for windows then reboot: reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\TimeZoneInformation" /v RealTimeIsUniversal /t REG_DWORD /d 1 /f .reg file is: Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00 [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\TimeZoneInformation] "RealTimeIsUniversal"=dword:00000001 To return to default: reg delete "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\TimeZoneInformation" /v RealTimeIsUniversal /f or reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\TimeZoneInformation" /v RealTimeIsUniversal /t REG_DWORD /d 0 /f .reg file is: Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00 [-HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\TimeZoneInformation\RealTimeIsUniversal] If you would like to have more accurate time in windows, Load this in Registry: Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00 [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\W32Time\Config] "FrequencyCorrectRate"=dword:00000002 "MaxPollInterval"=dword:0000000a "MinPollInterval"=dword:00000006 "UpdateInterval"=dword:00000064 [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\W32Time\Parameters] "NtpServer"="0.us.pool.ntp.org 1.us.pool.ntp.org 2.us.pool.ntp.org 3.us.pool.ntp.org" [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\W32Time\TimeProviders\NtpClient] "SpecialPollInterval"=dword:00000040 Run these commands in an administrator cmd window. Not a power shell window. Click start, type cmd, then click run as administrator: sc config W32Time start=auto net start W32Time w32tm /query /configuration w32tm /query /status time /t w32tm /resync To Put things back: sc config W32Time start=demand net stop W32Time Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00 [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\W32Time\Config] "FrequencyCorrectRate"=dword:00000004 "MaxPollInterval"=dword:0000000f "MinPollInterval"=dword:0000000a "UpdateInterval"=dword:00057e40 [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\W32Time\Parameters] "NtpServer"="time.windows.com,0x9" [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\W32Time\TimeProviders\NtpClient] "SpecialPollInterval"=dword:00008000
request the Payee to add their EFT details via the Online Donations system
More people are using the tools app to submit receipts to the clerk than ever before. If your ward clerk is unable to process the expense reimbursement request you submitted electronically with your phone due to the error message "No EFT details exist for this Participant for the Payment Type selected. Please select a different Payment Type or request the Payee to add their EFT details via the Online Donations system." This is what you need to do:
Open the web browser of your choice:
Go to the church web site: https://www.churchofjesuschrist.org/
Log in to your account:
Top Right corner:
Sign In:
Pass Raw Physical disks on a windows host to a linux virtualbox
ThanksWith the VM shut down, and all managers and services like VBoxVmService stopped: Optional when disk numbers have changed: Delete the existing TINY vmdk files with the same exact names you will be re creating from the file system and inside the .vbox file Open power shell prompt as admin then run the following: cd 'C:\Program Files\Oracle\VirtualBox\' .\VBoxManage internalcommands createrawvmdk -filename "C:\0.vmdk" -rawdisk \\.\PhysicalDrive0 .\VBoxManage internalcommands createrawvmdk -filename "C:\1.vmdk" -rawdisk \\.\PhysicalDrive1 .\VBoxManage internalcommands createrawvmdk -filename "C:\2.vmdk" -rawdisk \\.\PhysicalDrive2 .\VBoxManage internalcommands createrawvmdk -filename "C:\3.vmdk" -rawdisk \\.\PhysicalDrive3 .\VBoxManage internalcommands createrawvmdk -filename "C:\4.vmdk" -rawdisk \\.\PhysicalDrive4 ..... How ever many you have Add the disks back in to the VM definition using the GUI. Be sure you do not use any disks that windows might try to use. Test the VM, boot, run, power off restart the services like VBoxVmService
Ubuntu 20.04 LTS 64 on a Raspberry Pi 4
ThanksInstall Ubuntu Server on a Raspberry Pi 2, 3 or 4 https://ubuntu.com/download/raspberry-pi Scan your LAN to find the IP then SSH ssh -p 22 [email protected] Password is ubuntu Set Time zone: dpkg-reconfigure tzdata Configure your advanced network: If using Netplan: https://netplan.io/examples If using NetworkManager: apt install network-manager nmtui If you get the error: Connection is not available on device eth0 because device is strictly unmanaged find related config files of interest: grep -r eth0 /etc/ Comment out everything, or delete file: vi /etc/netplan/50-cloud-init.yaml vi /etc/netplan/01-netcfg.yaml # This file describes the network interfaces available on your system # For more information, see netplan(5). # Set and change netplan renderer to NetworkManager GUI tool network: version: 2 renderer: NetworkManager reboot root@rpi4-ubuntu:~# grep -r eth0 /etc/ /etc/initramfs-tools/initramfs.conf:# Specify a specific network interface, like eth0 /etc/NetworkManager/system-connections/eth0 no VLAN.nmconnection:id=eth0 no VLAN /etc/NetworkManager/system-connections/eth0 no VLAN.nmconnection:interface-name=eth0 /etc/NetworkManager/system-connections/VLAN connection 1.nmconnection:interface-name=eth0.5 /etc/NetworkManager/system-connections/VLAN connection 1.nmconnection:parent=eth0 /etc/dhcp/dhclient.conf:# interface "eth0"; /etc/dhcp/dhclient.conf:# interface "eth0"; /etc/netplan/50-cloud-init.yaml:# eth0: root@rpi4-ubuntu:~#
STMicroelectronics Joystick in FS Mode
Son's flight controller not connecting to his simulator under Windows 10.
This is how we tested the hardware under linux:
$ lsusb | grep -i joy
Bus 001 Device 006: ID 0483:5710 STMicroelectronics Joystick in FS Mode
$
$ sudo apt install joystick
$ ls /dev/input/by-id/*-joystick
/dev/input/by-id/usb-FrSky_FrSky_Taranis_Joystick_00000000001B-event-joystick /dev/input/by-id/usb-FrSky_FrSky_Taranis_Joystick_00000000001B-joystick
$
$ jstest /dev/input/by-id/usb-FrSky_FrSky_Taranis_Joystick_00000000001B-joystick
Driver version is 2.1.0.
Joystick (FrSky FrSky Taranis Joystick) has 7 axes (X, Y, Z, Rx, Ry, Rz, Throttle)
and 24 buttons (BtnA, BtnB, BtnC, BtnX, BtnY, BtnZ, BtnTL, BtnTR, BtnTL2, BtnTR2, BtnSelect, BtnStart, BtnMode, BtnThumbL, BtnThumbR, ?, (null), (null), (null), (null), (null), (null), (null), (null)).
Testing ... (interrupt to exit)
Axes: 0: 20606 1: 16215 2: 16552 3: 16215 4: 0 5: 0 6: 0 Buttons: 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:off 4:off 5:off 6:off 7:off 8:off 9:off 10:off 11:off 12:off 13:off 14:off 15:off 16:off 17:off 18:off 19:off 20:off 21:off 22:off 23:off ^C
$
$ lsusb -v -d 0483:5710
Bus 001 Device 006: ID 0483:5710 STMicroelectronics Joystick in FS Mode
Device Descriptor:
bLength 18
bDescriptorType 1
bcdUSB 2.00
bDeviceClass 0 (Defined at Interface level)
bDeviceSubClass 0
bDeviceProtocol 0
bMaxPacketSize0 64
idVendor 0x0483 STMicroelectronics
idProduct 0x5710 Joystick in FS Mode
bcdDevice 2.00
iManufacturer 1 FrSky
iProduct 2 FrSky Taranis Joystick
iSerial 3 00000000001B
bNumConfigurations 1
Configuration Descriptor:
bLength 9
bDescriptorType 2
wTotalLength 34
bNumInterfaces 1
bConfigurationValue 1
iConfiguration 0
bmAttributes 0xe0
Self Powered
Remote Wakeup
MaxPower 100mA
Interface Descriptor:
bLength 9
bDescriptorType 4
bInterfaceNumber 0
bAlternateSetting 0
bNumEndpoints 1
bInterfaceClass 3 Human Interface Device
bInterfaceSubClass 0 No Subclass
bInterfaceProtocol 0 None
iInterface 0
HID Device Descriptor:
bLength 9
bDescriptorType 33
bcdHID 1.11
bCountryCode 0 Not supported
bNumDescriptors 1
bDescriptorType 34 Report
wDescriptorLength 54
Report Descriptors:
* UNAVAILABLE *
Endpoint Descriptor:
bLength 7
bDescriptorType 5
bEndpointAddress 0x81 EP 1 IN
bmAttributes 3
Transfer Type Interrupt
Synch Type None
Usage Type Data
wMaxPacketSize 0x000b 1x 11 bytes
bInterval 10
Device Status: 0x0001
Self Powered
$
Thanks
Mount dd dump of disk in linux or other remote storage represented as a file.
ThanksSo you have a remote storage or a file based dd backup and you want to mount a part of it in the middle. # parted /dev/mapper/hitachi_asdf1 unit b print Model: Linux device-mapper (linear) (dm) Disk /dev/mapper/hitachi_asdf1: 42949672960B Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/512B Partition Table: gpt Number Start End Size File system Name Flags 1 1048576B 26214399B 25165824B primary bios_grub 2 26214400B 235929599B 209715200B primary msftdata 3 235929600B 445644799B 209715200B ext2 primary msftdata 4 445644800B 20913848319B 20468203520B primary msftdata 5 20913848320B 42871029759B 21957181440B primary msftdata 6 42871029760B 42892001279B 20971520B primary msftdata # # mount -o ro,loop,offset=235929600 /dev/mapper/hitachi_asdf1 /mnt # # losetup --offset 235929600 /dev/loop2 /dev/mapper/hitachi_asdf1 # fsck /dev/loop2
Calibrating low cost Software Defined Radios like the r820t
- Local LTE carriers are carefully frequency corrected. You will see a quiet spot in the energy right in the center. Example: 737,000,000 Hz
- TV Carriers have a ATSC pilot that is very distinct and easy to tune to. Examples: 470,309,441 Hz and 174,306,000 Hz
ethernet > tcpdump > Linux > ssh > Windows > wireshark
"C:\Program Files\PuTTY\plink.exe" -batch -ssh -P 22 [email protected] "/usr/bin/sudo /usr/sbin/tcpdump -s 0 -i enp2s0 -w - 'port not 22'" | "C:\Program Files\Wireshark\Wireshark.exe" -i -
Should work with much older and newer of all components but tested with Ubuntu 18.04, Putty 0.70, WireShark 2.6.1, Windows 10 Pro 1803 17134.112
Adding -batch to prevent "Data written to the pipe is neither in a supported pcap format nor in pcapng format" error.
Thanks:
https://www.chiark.greenend.org.uk/~sgtatham/putty/latest.html
https://www.wireshark.org/download.html
Generating a Google Sunset Calendar using R on Ubuntu
https://www.timeanddate.com/sun/usa/parowan
https://hilaryparker.com/2014/05/27/sunsets-in-google-calendar-using-r/
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/how-to-install-r-on-ubuntu-16-04-2
http://blog.samsandberg.com/2014/06/04/sunsets-in-google-calendar-for-r-noobs/
sudo apt-key adv --keyserver keyserver.ubuntu.com --recv-keys E298A3A825C0D65DFD57CBB651716619E084DAB9
#sudo add-apt-repository 'deb [arch=amd64,i386] https://cran.rstudio.com/bin/linux/ubuntu trusty/'
#sudo add-apt-repository 'deb [arch=amd64,i386] https://cran.rstudio.com/bin/linux/ubuntu xenial/'
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgrade
sudo apt install r-base
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/hilaryparker/hilary/master/R/create_sunset_cal.R
vi create_sunset_cal.R
sudo -i R
install.packages("StreamMetabolism")
library(StreamMetabolism)
install.packages("gpclib")
library(maptools)
source("/YourPath/create_sunset_cal.R")
create_sunset_cal()
q()
head /YourPath/sunset.csv
Subject,Start Date,Start Time,End Date,End Time,All Day Event,Description,Location,Private
Sunset,2017-09-03,19:47:54 PM,2017-09-03,20:27:54 PM,False,Sunset Calendar,YourAddress,False
Sunset,2017-09-04,19:46:24 PM,2017-09-04,20:26:24 PM,False,Sunset Calendar,YourAddress,False
Sunset,2017-09-05,19:44:54 PM,2017-09-05,20:24:54 PM,False,Sunset Calendar,YourAddress,False
cat /YourPath/create_sunset_cal.R
#' Create a sunset calendar
#'
#' This function creates a .CSV of sunset appointments--with a user-specified location--that can be imported into Google Calendar.
#' @param date Date at which you want the calendar to start, in yyyy/mm/dd format.
#' @param lat Latitude of location (for sunset time calculation)
#' @param long Longitude of location (for sunset time calculation, will be negative for continental US)
#' @param timezone Timezone of location (for sunset time calculation).
#' @param num.days Number of days you want sunset appointments for.
#' @param file Filename for outputted .CSV file (to be uploaded to Google Calendar).
#' @param location Location of sunset appointment. Will be input into Google Calendar event as the event location.
#' @importFrom StreamMetabolism sunrise.set
#' @export
#' @examples \dontrun{
#' create_sunset_cal(location = "40.7127, -74.0059")
#'}
#'
create_sunset_cal <- function(date="2017/09/03",
lat = 40.7127,
long = -74.0059,
timezone = "America/Denver",
num.days = 365,
file="sunset.csv",
location = "YourAddress"){
location <- gsub(",", "", location)
dates <- seq(
as.Date(date),
by = "day",
length.out = num.days
)
sunset_times <- sunrise.set(
lat = lat,
long = long,
date = date,
timezone = timezone,
num.days = num.days
)$sunset
nms <- c(
'Subject',
'Start Date',
'Start Time',
'End Date',
'End Time',
'All Day Event',
'Description',
'Location',
'Private'
)
mat <- matrix(
nrow = length(dates),
ncol = length(nms)
)
mat <- data.frame(mat)
colnames(mat) <- nms
mat$Subject <- "Sunset"
mat$"Start Date" <- dates
mat$"End Date" <- dates
mat$"All Day Event" <- "False"
mat$Description <- "Sunset Calendar"
mat$Location <- location
mat$Private <- "False"
starts <- strftime(sunset_times-60*10, format="%H:%M:%S %p")
ends <- strftime(sunset_times+60*30, format="%H:%M:%S %p")
mat$"Start Time" <- starts
mat$"End Time" <- ends
write.csv(
mat,
file=file,
quote=FALSE,
row.names=FALSE
)
}
Time problems when dual booting Ubuntu Linux and Windows 10
Change Windows 10:
or
Make Linux use 'Local' time
Pre-Ubuntu 15.04 systems (e.g. Ubuntu 14.04 LTS):
- edit /etc/default/rcS
- add or change the following section
# Set UTC=yes if your hardware clock is set to UTC (GMT) UTC=no
Ubuntu 15.04 systems and above (e.g. Ubuntu 16.04 LTS):
- open a terminal and execute the following command
timedatectl set-local-rtc 1
timedatectl set-timezone America/Denver
timedatectl
dpkg-reconfigure tzdata
systemd upstart sysvinit start stop service
Perhaps this will help:
/usr/lib/systemd tells you you're on a systemd based system.
/usr/share/upstart is a pretty good indicator that you're on an Upstart-based system.
/etc/init.d tells you the box has SysV init in its history
The init process is always assigned PID 1. The /proc filesystem provides a way to obtain the path to an executable given a PID.
In other words:
nathan@nathan-desktop:~$ sudo stat /proc/1/exe
File: '/proc/1/exe' -> '/sbin/upstart'
As you can see, the init process on my Ubuntu 14.10 box is Upstart. Ubuntu 15.04 uses systemd, so running that command instead yields:
nathan@nathan-gnome:~$ sudo stat /proc/1/exe
File: '/proc/1/exe' -> '/lib/systemd/systemd'
If the system you're on gives /sbin/init as a result, then you'll want to try statting that file:
nathan@nathan-gnome:~$ sudo stat /proc/1/exe
File: '/proc/1/exe' -> '/sbin/init'
nathan@nathan-gnome:~$ stat /sbin/init
File: ‘/sbin/init’ -> ‘/lib/systemd/systemd’
You can also execute it to find out more:
[user@centos ~]$ /sbin/init --version
init (upstart 0.6.5)
So this is the newer in Ubuntu:
Starting with Ubuntu 15.04, Upstart will be deprecated in favor of Systemd. With Systemd to manage the services we can do the following:
systemctl start SERVICE - Use it to start a service. Does not persist after reboot
systemctl stop SERVICE - Use it to stop a service. Does not persist after reboot
systemctl restart SERVICE - Use it to restart a service
systemctl reload SERVICE - If the service supports it, it will reload the config files related to it without interrupting any process that is using the service.
systemctl status SERVICE - Shows the status of a service. Tells whether a service is currently running.
systemctl enable SERVICE - Turns the service on, on the next reboot or on the next start event. It persists after reboot.
systemctl disable SERVICE - Turns the service off on the next reboot or on the next stop event. It persists after reboot.
systemctl is-enabled SERVICE - Check if a service is currently configured to start or not on the next reboot.
systemctl is-active SERVICE - Check if a service is currently active.
systemctl show SERVICE - Show all the information about the service.
sudo systemctl mask SERVICE - Completely disable a service by linking it to /dev/null; you cannot start the service manually or enable the service.
sudo systemctl unmask SERVICE - Removes the link to /dev/null and restores the ability to enable and or manually start the service.
Virtual Audio Patching in Windows
I first found Jack audio on Linux, this video shows it on Windows. Simple use may only need the ASIO Bridge, for that skip to 10m49s
HERE ARE THE LINKS MENTIONED IN THIS VIDEO:
1. download for windows version of JACK AUDIO CONNECTION KIT
http://jackaudio.org/downloads/
2. tutorial on installing JACK AUDIO on windows
http://www.jackaudio.org/faq/jack_on_windows.html
3. download for KXSTUDIO Carla, and Cadence(Catia) for windows
http://kxstudio.sourceforge.net/Downloads
5. download VB-AUDIO ASIO BRIDGE
http://vb-audio.pagesperso-orange.fr/Cable/
6. download ASIO4ALL (optional) if you don't have a "true" ASIO SOUND CARD
http://www.asio4all.com/
In SDR, you may need to patch from one application to another. Here are some other ways to do it:
http://www.rtl-sdr.com/a-list-of-5-free-virtual-audio-cable-software-programs/
PCAP over IP to NetworkMiner
On NetworkMiner:
File > Receive Pcap over IP > Start
On your router:
Where:dumpcap -i eth0 -P -w - -f "ether host 90:b6:86:24:61:86" | nc 10.0.5.2 57012
eth0 = The interface.vlan you want to capture. Leave the vlan off to capture all vlans and the vlan tags.
eth0.4 = Capture vlan 4 on the first physical ethernet interface.
90:b6:86:24:61:86 = The MAC address of the device you want
10.0.5.2 = The host running NetworkMiner (Do Not capture the traffic you are streaming. Loop)
57012 = the port NetworkMiner is listening on.

Install Grub
#Dump the Windows key from a PC Motherboard to use in your windows VM after you get linux installed: tail -c+57 /sys/firmware/acpi/tables/MSDM #Local Disk Copy with progress indicator, but not verbose file by file detail: rsync -aSWxHAX --info=progress2 --numeric-ids /source-dir/ /target-dir/ #mount the partitions you use, skip those you do not sudo mount /dev/sdXY /mnt sudo mount /dev/sdXY /mnt/boot sudo mount /dev/sdXY /mnt/boot/efi #Mount the critical virtual file systems. Run the following as a single command: for i in /dev /dev/pts /proc /sys /run; do sudo mount -B $i /mnt$i; done #Chroot into your normal system device: sudo chroot /mnt #Reinstall GRUB 2 (substitute the correct device with sda, sdb, etc. #Do not specify a partition number): grub-install /dev/sdX #Recreate the GRUB 2 menu file (grub.cfg) update-grub #Exit chroot: CTRL-D on keyboard #Reboot. sudo reboot